What is Wheatstone Bridge ?
Wheatstone Bridge is an instrument designed to measure unknown resistance in electrical circuits. It calculates the unknown resistance by balancing the two legs of the bridge circuit where one leg contains both known resistors and the other leg contains one known (variable) and one unknown resistor.
- Since it estimates unknown resistance in an electric circuit, it is also known as a resistance bridge.
- Wheatstone bridge is a very reliable instrument as it measures the resistance very precisely.

Wheatstone Bridge Principle
Wheatstone Bridge works on the principle of null deflection i.e., there is no current flowing through the galvanometer, and its needle shows no deflection, hence the name null deflection. In the unbalanced state of the Wheatstone bridge i.e., when the potential across the galvanometer is different, the galvanometer shows the deflection, and as the bridge becomes balanced by changing the variable resistor, the potential difference across the galvanometer becomes zero i.e., the equilibrium state of Wheatstone bridge.
Construction of Wheatstone Bridge
Construction of Wheatstone Bridge requires four resistors P, Q, R, and S that are placed in the form of four sides AB, BC, AD, and DC of a quadrilateral ABCD. A cell E and key K1 are placed between the A and C ends of this quadrilateral, and a sensitive galvanometer G and key K2 is placed between the B and D ends. Clearly, the potential of point A will be equal to the potential of the positive plate of the cell and the potential of point C will be equal to the potential of the negative plate of the cell.
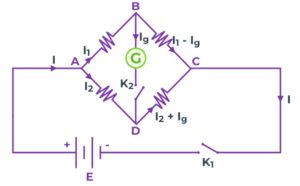
It is clear from the figure that the resistances P and Q are in series when the key K2 is open. Similarly, resistances R and S are in series, but P and Q together (arm ABC) and R and S together (arm ADC) are connected in parallel to each other. Since the side BD of the galvanometer is placed like a bridge over the sides ABC and ADC of the quadrilateral, this circuit is called a bridge.
When the bridge is in an equilibrium state, that is, there is no deflection in the galvanometer. That is, in the equilibrium state of the bridge, the ratio of the resistances of any two adjacent arms is equal to the ratio of the remaining two adjacent sides.
Advantages of Wheatstone’s Bridge
- With the help of Wheatstone’s Bridge, we can build a Meter bridge.
- We can measure minute changes in the bridge, even in m ohm.
- We can measure strain and pressure using a Wheatstone bridge.
Disadvantages of Wheatstone’s Bridge
- The result of Wheatstone’s Bridge can be easily affected by temperature and EMF cells.
- Wheatstone Bridge fails if it is not in a balanced condition.
- The cost of maintaining the Wheatstone Bridge is very high.